101
Published on Jun. 4th 2025
Reverse Engineering with 3D Scanning: Faster, Smarter, Easier
Learn how 3D scanning transforms CAD reverse engineering. Explore tools, workflows, and real-world 3D scan to CAD applications in design and manufacturing.
Reverse engineering is essential in industries like automotive, engineering machinery, heavy industry, enabling makers and engineers to recreate, modify, or enhance existing components. But traditional reverse engineering methods can be slow and error-prone. However, CAD reverse engineering combined with modern 3D scan to CAD workflows changes the game—delivering speed, accuracy, and seamless digital capture.
In this guide, we’ll explore how 3D scanning transforms reverse engineering, the best tools available for scan-to-CAD conversion, and real-world applications that showcase its impact.

1. What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering, also known as back engineering, is the process of analyzing and reproducing a part or system. Reverse engineering extracts design information directly from existing objects, then disassembling, examining, and digitally reconstructing it into an accurate 3D model.
Common applications:
- Optimizing designs by analyzing competitors’ products
- Recreating obsolete parts for industrial machinery or classic vehicles
- Repairing or replacing worn-out components
- Customizing parts, accessories, and modifications
But extracting design data isn’t always easy—especially with traditional methods.
2. Manual Reverse Engineering vs. 3D Scanning
Traditional reverse engineering often relies on manual measurement tools such as calipers or CMMs. While effective for simple geometries, these reverse engineering techniques present several limitations:
❌ Low efficiency: Measuring complex parts by hand is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
❌ Inaccuracy: Manual errors and limited sampling points lead to poor dimensional fidelity.
❌ Poor adaptability: It’s difficult to capture freeform surfaces, organic shapes, or hard-to-reach features.
3D scanning addresses these issues by capturing the full surface geometry of an object—quickly, accurately, and without physical contact. Whether you’re working with worn-out components, curved surfaces, or intricate assemblies, 3D scanners enable an efficient 3D scan to CAD workflow, delivering a complete and high-resolution digital model. This greatly improves the reverse engineering workflow, making it smoother, more reliable, and suitable for reverse engineering in manufacturing and product development.
Let’s take a closer look at how the reverse engineering workflow using 3D scanning works.
3. Step-by-Step Reverse Engineering Process with 3D Scanning
Let’s take SHINING 3D’s EinScan Libre—an all-in-one, standalone, and wireless 3D scanner—as an example.
Step 1: Scan the object
Engineers capture the object’s surface geometry within minutes with EinScan Libre.
Step 2: Generate a high-quality mesh
The scanned point cloud data is converted into a watertight mesh (STL file), which can be cleaned and refined directly on the device—powered by a high-performance NVIDIA processor and a 5.5-inch touchscreen for smooth, responsive operation.
Step 3: Convert mesh to CAD
With seamless integration to EXModel via EXScan Libre, the mesh data can be transformed into an editable parametric CAD model in just one click.
Step 4: Analyze, optimize & manufacture
The final CAD model enables engineers to:
✔ Adjust dimensions for improved performance
✔ Perform stress analysis using CAE software
✔ Export CAD-ready files for downstream processes such as CNC machining, injection molding, or 3D printing

4. Recommended Software for Reverse Engineering CAD Models
EXModel serves as a powerful bridge between 3D scanning and CAD modeling, streamlining the reverse engineering process from scan to production. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools to generate professional-grade, parametric CAD models compatible with mainstream CAD platforms.
Fully integrated into SHINING 3D’s scanning workflow, EXModel allows for one-click data transfer from the scanning software, enabling a fast and seamless transition from mesh to CAD.
Many users apply SHINING 3D scanners and EXModel for bumper customization, yacht design, mold optimization which lost the original CAD files, and so on.

EXModel
EXModel is a powerful gateway that simplifies CAD modeling, from 3D scanning to manufacturing. It provides a comprehensive set of tools that enable you to transform a mesh into a professional-quality CAD solid model in just a few simple steps.
- EXModel: The bridge between 3D scanning mesh and CAD design
- EXModel Pro: All-in-one reverse engineering solution
Many users rely on SHINING 3D scanners and EXModel for CAD reverse engineering in a wide range of applications. These range from bumper customization and automotive component replication to yacht design and mold optimization when original CAD files are missing. Other common uses include heritage preservation and restoration, medical prosthetics design, and product development for consumer electronics.
5. 3D Scanning Use Cases in Reverse Engineering Across Industries
Automotive
Reverse engineering plays a critical role in the automotive industry by enabling rapid redesign, optimization, and reproduction of complex components. Through 3D scanning and reverse engineering, manufacturers can accurately capture existing parts for design improvement, aftermarket customization, legacy part replacement, and competitive benchmarking.
Reverse engineering rescue vehicles with high-accuracy 3D scanning
Blue Sky Rescue leveraged SHINING 3D's metrology scanners—FreeScan Trak Pro2 and FreeScan Combo Series—to reverse engineer vehicle interiors. By digitally capturing complex geometries, the team optimized layouts and rapidly integrated custom equipment, boosting efficiency in emergency response.
Reverse engineering a Porsche for Restoration
Spain Porsche restoration expert Juliá Automobile leveraged SHINING 3D's FreeScan Trak ProW to complete a high-accuracy reverse engineering project for a 1995 Porsche 993.

Engineering Machinery & Other Transportation
In engineering machinery and transportation sectors such as rail, marine, and construction equipment, reverse engineering enables the digital reconstruction of large, worn, or undocumented components. It supports maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations by allowing obsolete or damaged parts to be reproduced without original drawings. Reverse engineering also helps optimize structural performance, reduce downtime, and modernize legacy systems while ensuring compatibility with existing assemblies.
Enhancing yacht customization with EinScan Libre
Custom Marine Solutions adopted SHINING 3D’s wireless EinScan Libre 3D scanner to enhance their yacht accessory creation process. By scanning yachts in outdoor environments, they were able to create custom-fit accessories like carpets and upholstery more efficiently, improving accuracy and reducing labor.

Repairing Forging Dies
The case describes a new approach to forging die repair that combines the 3D scanner with the industrial robot to improve the efficiency and precision of die repair.

Energy & Heavy Industry & Public Utilities
For energy, heavy industry, and public utilities, reverse engineering is essential for asset lifecycle management. Large-scale equipment such as turbines, pipelines, valves, and power-generation components can be digitized to assess wear, deformation, and failure risks. Reverse engineering supports retrofit projects, performance optimization, and compliance verification, while minimizing costly shutdowns and extending the service life of critical infrastructure.
Empowering mining equipment reverse engineering
GL Equipamentos, specializing in reverse engineering mining equipment parts, faced inefficiencies with traditional manual measurement methods. By adopting SHINING 3D’s high-accuracy scanners, they enhanced measurement accuracy and significantly reduced data collection time for reverse engineering.

Electronic & Electrical
In the electronic and electrical industry, reverse engineering enables precise reconstruction of housings, connectors, and internal structures to support product redesign, miniaturization, and functional optimization. It is widely used in product iteration, enclosure fitting, thermal management optimization, and compatibility testing. By converting physical components into accurate digital models, reverse engineering accelerates innovation while ensuring tight tolerances and integration accuracy.
Civil Aviation
Reverse engineering is widely applied in civil aviation for inspection, repair, and certification support of high-value, safety-critical components. Aircraft parts can be scanned to detect deformation, wear, or manufacturing deviations, and then reconstructed into precise CAD models for analysis and remanufacturing. This process supports maintenance efficiency, spare part reproduction, and structural validation while meeting strict regulatory and quality requirements.
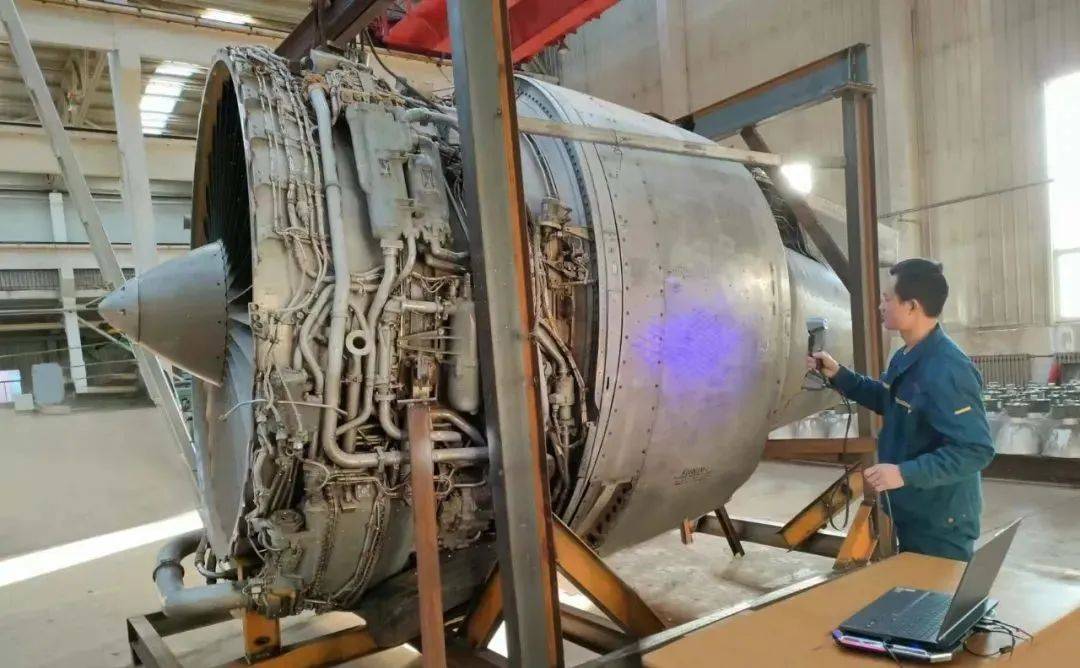
Rapid Reverse Engineering for Aircraft Engine MRO
An aircraft MRO provider uses the SHINING 3D FreeScan UE laser scanner to capture complex, non-standard engine parts, creating digital blueprints for rapid, high-accuracy repair and fabrication.

Medical & Basic Research
In medical and research fields, reverse engineering enables the creation of highly accurate anatomical models and customized medical devices. Patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and surgical guides can be designed by reverse engineering scanned anatomical data. In basic research, it supports experimental validation, biomechanical analysis, and digital modeling of complex biological or experimental structures, improving precision and reproducibility.
Driving 3D Technology Standardization in Orthotics and Prosthetics
Lammert Scherer GmbH uses SHINING 3D’s EinScan H2 and AccuFab L4K to streamline prosthetic design, ensure accuracy, and enhance patient comfort through digital workflow.

Cultural Creation & Art Customization
Reverse engineering empowers cultural creation and art customization by enabling the digital preservation, reproduction, and transformation of physical artworks and cultural artifacts. High-resolution 3D scanning allows artists and designers to modify, scale, or replicate sculptures, ornaments, and handcrafted objects while preserving original details. It also supports digital archiving, restoration, and creative reinterpretation for exhibitions, customization, and commercial applications.
Preserve and Reconstruct Oracle Bone Inscriptions
High-precision 3D scanning technology is revolutionizing the preservation of ancient oracle bones—capturing detailed inscriptions, enabling digital rubbings, and bringing early Chinese civilization to life through immersive digital models.

Research & Education
In research and education, reverse engineering serves as a powerful tool for teaching design principles, manufacturing processes, and engineering analysis. Students and researchers can study real-world objects by converting them into digital models for simulation, redesign, and performance evaluation. This hands-on approach bridges theory and practice, fostering innovation, problem-solving skills, and interdisciplinary learning across engineering and scientific disciplines.
Build Dinosaur Models from Fossils
Dr. Fernando Novas and Prof. Marcelo Pablo Isasi used 3D scanning and printing to digitally reconstruct Taurovenator, a Cretaceous predator from Argentina, advancing fossil research and preservation.

6. Conclusion
As industries push for faster development cycles and more accurate manufacturing, 3D scanning has become an indispensable tool for reverse engineering. With advanced 3D scanners, engineers can scan intricate parts in seconds, generate high-accuracy CAD models, and accelerate product innovation. This approach offers several key benefits:
- Cost-effectivesolutions
- Perfect for complex structures
- Accelerated design and optimization
Ready to transform your reverse engineering process? Get a free consultation with the SHINING 3D expert team today.
